Below you will find information about the different methods used to "abort" a developing embryo or fetus - including suction curettage (vacuum aspiration), chemical abortion (abortion pill), curettage, as well as feticide.
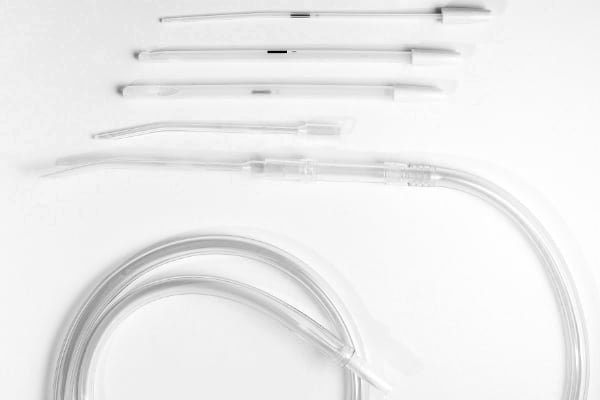

The suction method is the most frequently performed abortion method in Germany. The process begins with the opening and stretching of the cervix with special metal pins. The doctor then inserts a suction tube, whose suction power is 10-30 times stronger than a vacuum cleaner, into the uterus.
The tube sucks out the amniotic fluid, placenta, unborn child, and the uterus' mucous membrane, tearing the body of the unborn child into pieces. Afterward, the doctor checks by ultrasound whether fragments of the embryo have remained in the uterus. To prevent inflammation from developing, these are removed, if necessary, by further suction or a curette.
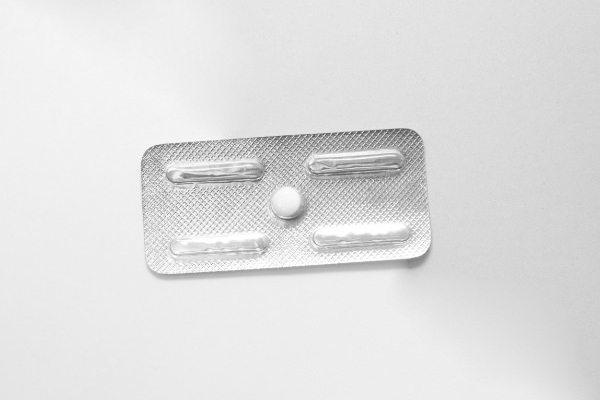

The abortion pill is a medication method of inducing an abortion and can be taken until the 63rd day after the last menstrual period. The drug blocks the pregnancy-maintaining hormone progesterone. As a result, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the unborn child is interrupted.
After 36 to 48 hours, the child dies. About two days later, the mother takes another tablet (misoprostol). This tablet induces contractions so that the unborn child and the placenta are expelled. This often results in very heavy bleeding.
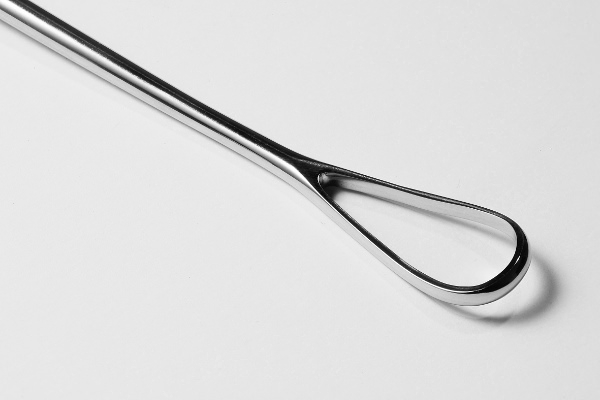

During curettage, the cervix is dilated with special pins. Then the doctor inserts the curette (a metal spoon-like instrument) through the vagina into the uterus, scraping the uterine wall. In the process, the body of the unborn child is torn into pieces and transported out.
Cervical curettage is no longer widely used as the sole abortion method because the mother's risk of injury is greater than with other methods.
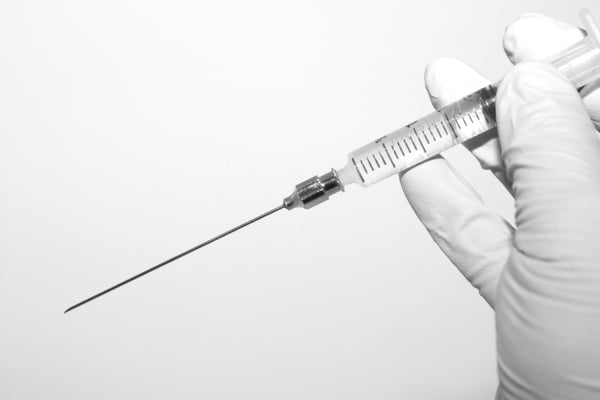
Fetocide is a late-term abortion method. The method is used at a time when the child would already be viable outside the womb. In this method, the doctor pierces the woman's abdominal wall with a long needle to reach the abdominal cavity.
Using ultrasound vision, he then searches for the baby's heart, which is about the size of a cherry pit. When he finds it, he sticks the long needle and injects a potassium chloride solution into it. The solution causes the unborn child's heart to stop immediately. Then the killed child is delivered traditionally.